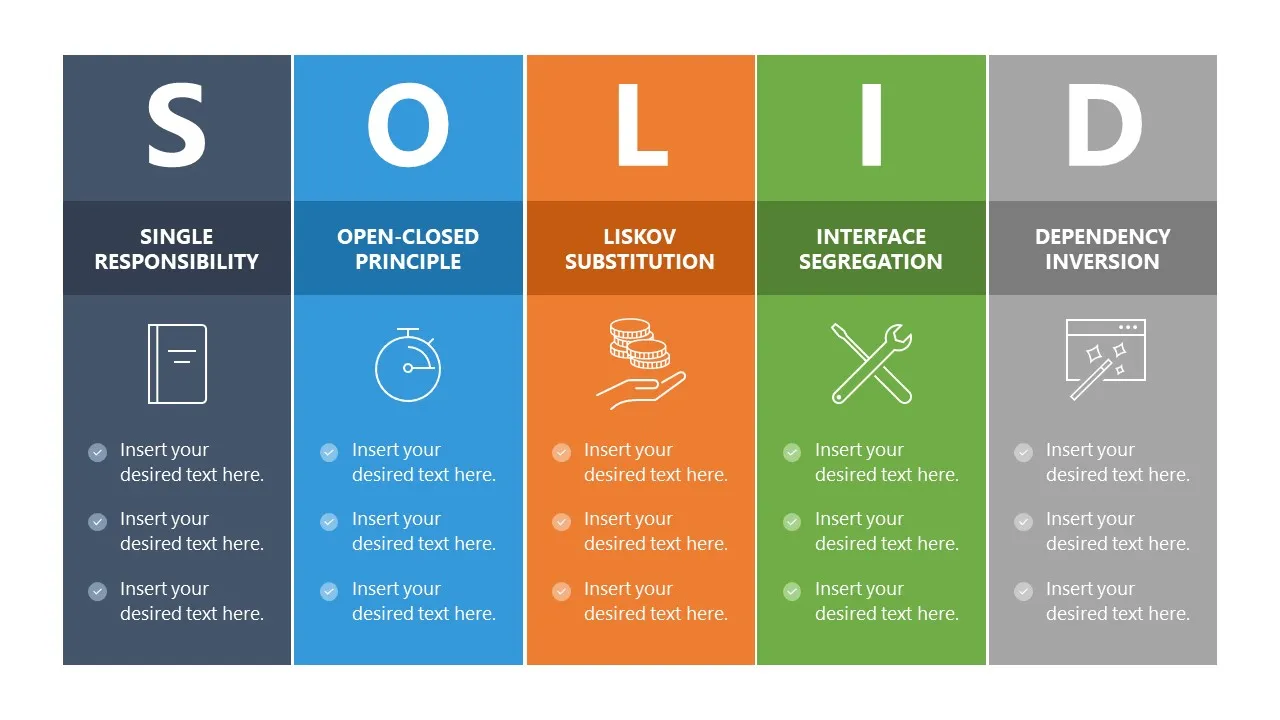
SOLID Principle and Design Patterns
SOLID abbreviation represents :
SRP(Single Responsibility Principle) - A class should have only one responsibility.
OCP(Open Closed Principle) - Software entities should be open for extension, but closed for modification
LSP(Liskov Substitution Principle) - Functions that use pointers or references to base classes must be able to use objects of derived classes.
ISP(Interface Segregation Principle) - Interfaces can be segregated for clients not depending on interfaces that they do not use.
DIP(Dependency Inversion Principle) - Depend upon abstractions, not concretes.
Essential attributes of good software
Maintainability :
Software should be written in such a way so that it can evolve to meet the changing needs of customers. This is a critical attribute because software change is an inevitable requirement of a changing business environment.
Dependability and security :
Software dependability includes a range of characteristics including reliability, security and safety. Dependable software should not cause physical or economic damage in the event of system failure. Malicious users should not be able to access of damage the system.
Efficiency :
Software should not make wasteful use of system resources such as memory and processor cycles. Efficiency therefore includes responsiveness, processing time, memory utilization, etc.
Acceptability :
Software must be acceptable to the type of users for which it is designed. This means that it must be understandable, usable and compatible with other systems that they use.