· Hankyu Kim · Filter · 2 min read
Average Filter
The average filter is the simplest form of recursive estimation. Despite its simplicity, it provides strong noise reduction and forms the foundation of more advanced filters such as the Kalman filter.

Introduction
This post introduces the Average Filter, one of the simplest yet most powerful tools in signal processing and estimation.
Although the idea of taking an average is trivial, expressing it as a recursive filter reveals a structure that appears throughout modern estimation theory, including the Kalman filter.
One-Sentence Definition
- Average Filter
An average filter updates an estimate by combining the previous average with the current measurement.
Basic Definition of an Average
Given samples, the arithmetic mean is defined as
For example,
This is the most familiar form of averaging.
Recursive Interpretation
Assume that the average of the first samples is already known:
When a new sample arrives, the updated average can be written as
This can be rewritten in a generic form:
where
Key Insight
- The average is updated incrementally
- Past information is not discarded
- The structure is inherently recursive
This recursive form is far more useful in real-time systems than recomputing the full sum at every step.
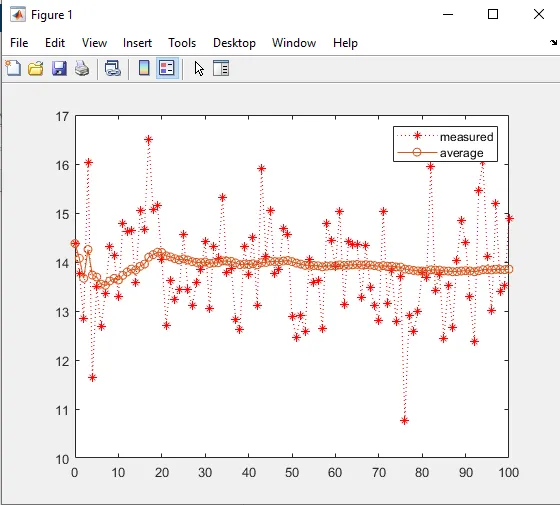
Example: Noisy Voltage Measurement
Consider a car battery with a true voltage of approximately 14V.
Due to sensor noise, the measured voltage fluctuates between 10V and 18V.
Assume:
- Sampling interval: 1 second
- Total duration: 100 seconds
Applying an average filter:
- Early estimates fluctuate significantly
- As more samples accumulate, the estimate stabilizes
- The filtered voltage converges toward 14V
Despite its simplicity, the average filter effectively suppresses noise.
General Average Filter Equation
The average filter can be expressed as
where:
- is the current estimate
- is the previous estimate
- is the current measurement
- is the weighting factor
This structure directly appears in:
- Exponential moving averages
- Low-pass filters
- Kalman filters
Why This Matters
- The average filter is the simplest recursive estimator
- All practical filters rely on recursion
- Understanding this structure is essential before studying Kalman filters
If the recursive nature of the average filter is not clear, advanced estimation methods will remain opaque.
Summary
- The average filter is simple but fundamental
- It combines past estimates with new measurements
- It provides effective noise reduction
- It forms the conceptual foundation of modern estimation theory
Simple mathematics, powerful implications.



